In 1904 the proud D.D. Methodist Robert William van Schroik, at the age of 61, boarded a German steamer in New York for a 70-day trip to the Holy Land. The cost was $550 to cover the entire trip on sea and land. The number of travelers on the ship was over 800. This was obviously not the first Protestant American pilgrimage to the Holy Land and the travel book that was produced is nowhere near the quality of the classic The Land and the Book, first published in 1859 by the American missionary William Thomson. Our 1904 journeyman called his book The Book and the Land, a pale reflection of the earlier classic. This tale of Sunday School biblical adventure has a dedication: “the bravest of all Crusaders and Discoverers, Christopher Columbus,” although the direction of sail was reversed. If you are not interested in reading the dull prose of this anti-classic, you can follow the highlights in the post below.

It took eight days to reach Madeira and the first major stop after Gibralter was at Algiers. The ship docked at 1:30 am while the intrepid traveler was taking a bath. Once ashore the fact that he did not know Arabic or French limited his visit. As he laments, “In two or three instances by motion of lips and hands, and even feet, I tried to make myself understood, but it was useless, and, like many others, I resigned myself to my environments.” He was very much the precursor of the “ugly American”, as shown in his comment on the Arabs of Algiers: “Our drive to the Arab quarters, where poverty, disease, imbecility, and squalor were much in evidence to our optical and olfactory senses, showed us how wide is the gulf which separates our Christian, Bible loving America from this country, where the inspired word of God is scarcely seen or read.” I am not sure if our Robert expected to find a Gideon Bible in his hotel room, but I suspect there was none since the Gideons did not start placing Bibles in hotels until 1908 and that was in Montana.
Like many other steamer-rolled Holy Land visitors, it was the idea of walking where Jesus had walked that excited this lay Methodist. For sure he was no “innocent abroad” in the wake of Mark Twain. He shared his steamer suite with two Presbyterians, a reverend and a missionary. As he explains, “We are all good travelers, untroubled by seasickness, and so far we have not missed a meal. We joke each other occasionally about our denominationalism but as all things are foreordained, according to their creed, and we Methodists have the right to choose the best on sea and land, I have chosen them to be good fellows to room with on a ship. So our Calvinism and Arminianism combine beautifully, and stateroom No. 628 is doing its full part to hasten the millennium.” Over a century later the hastening of the prophetic Millennium appears to be ongoing.
After scenic stops in Malta, Athens and Corinth, they reach Constantinople. Here there was a lecture that was greatly appreciated by our itinerant Methodist: “Mr. Pears ‘s lecture was especially fine in the information he gave concerning the museum where many of the relics are unmistakable proofs of those Bible statements most severely criticized. For example, the stone in the museum, positively from Solomon’s Temple, which speaks of the penalty imposed on those who profane the temple fully answers the criticisms of those who tell us that Jesus, a youth, could not have driven the people with a whip from the temple, as it would have created a riot throughout the city.” Whether or not the museum held the foreskin of Jesus is not mentioned. It should be noted that Charlemagne, who said the holy prepuce was given to him by an angel, presented the holy relic to Pope Leo III in 800 CE in exchange for recognition as king. Apparently it disappeared at a later time from Rome.
Eventually the tour reached Beirut, where some 21 brave ones took a train to Baalbek. Our traveler lists his companions: “Of the other members of our party, missionaries, preachers, bankers, business men, two were from Iowa, two from Illinois, one from Arkansas, one from Louisiana, two from Massachusetts, two from Smyrna, two from Beirut, one from Kansas, one from Oregon, one from Sidon, Syria, one from Toronto, Canada, one from Sofia, Bulgaria, three from Saint Louis, Mo., one from Ohio, and one from Michigan.” It was indeed a cosmopolitan group of pilgrims. Yet another lecture was provided, where it was noted that some people say Baalbek was founded by Cain some 133 years after the creation of Adam, although some suggest “Nimrud, the mighty hunter.” But here is the clincher: “There is little doubt that it is the Baalath where Solomon built a castle in honor of the Queen of Sheba, and where he also built a temple to please his concubines after he departed from the worship of God to the worship of Baal.” What a gentleman the ancient Israelite king was, taking care of his hundreds of lust-filled concubines after he got religion.
Arriving in Damascus they were put up in the luxurious Grand Hotel D’Orient of the Kaonan Brothers proprietors, but they quickly went into action. “We took carriages at once and drove to the street ‘called Straight’ and saw the house of Judas, the first house Paul visited in Damascus and where the scales fell from his eyes when Ananias put his hands upon him. Near this house was the fountain where Paul was baptized.” In the evening they watched the sunset at a place overlooking Damascus, which they were told was where Muhammad received his first revelation from Allah. And even more, “We also saw the maple tree, called ‘the tree of the holy prophet,’ said to be one thousand three hundred years old. It is of fifty feet girth, over sixteen feet diameter.” They also visited the grave of Fatima, Muhammad’s daughter. It was a very diligent interfaith agenda in this part of Syria.
Leaving Damascus, our emotional Methodist penned the following praise: “Damascus! Star and Crescent combined; Emerald of Syria; Eden of our first parents; Abraham’s mount of vision where he had his first revelation of God; where Paul, too, received the heavenly vision to which, like Abraham, he was not disobedient; where Mohammed got an intenser love for the paradise not of earth Damascus! May all that is noble, beautiful, and magnificent in thy long history be repeated and more than duplicated in all the coming ages, and all that has been dark, cruel, superstitious, and unworthy of thee be forever forgotten.” I suspect that this tribute has yet to be translated into Arabic.
Now the sacred object of the tour was close. “A whole book could be written of what we saw and thought at Nazareth, Galilee, and Samaria, where so much of our Saviour’s ministry was spent, but we must on to Jerusalem,” writes our impatient Methodist pilgrim. It was clearly not a whole book he chose to write. On the way the sites of biblical dimensions were almost everywhere. “Our guide pointed to the hill where Samson was born, but we learn that many other places contend for the honor of having been his birthplace.” Imagine that. Perhaps there was a lock of Samson’s hair back in the Istanbul museum.
In Jerusalem he first visited the American Colony, where he was served cake and hot tea. “As we sallied forth that which impressed me was the cosmopolitan character of the people I met. Jews, Arabs, English, French, Scotch, and Americans were to be seen, and twice as many other nationalities were represented,” notes our pilgrim. Now all of Bible history came to light. “I found here the sublime and ridiculous in most convenient juxtaposition. For example, here was the very spot from which the earth was taken out of which Adam was created, and just a few yards away was his tomb. Here was the very spot where the crucifixion occurred, the brass hole wherein the cross was placed marking the center of the earth and, in the cellar of the church, the shrine where Helena, mother of Constantine, discovered in a vision the true cross. Everything is here.” But, “the strangest thing of all is the credulity of thousands upon thousands who accept these claims with the utmost sincerity.” Then, he continues: “All the surroundings show the genuineness of the Bible narrative recorded in the fifth chapter of the gospel by John.” I believe he says this with the utmost sincerity.
Jerusalem is, of course, close to Jericho and the Dead Sea, so off our hero went. “I confess to some nervousness, as our carriage, drawn by three horses, would swing perilously near the precipitous cliffs below the roadway. To add to my trepidation, the drivers are proverbially careless, and often give free vent to their propensity for driving past the teams ahead of them.” It seems he survived, since he later wrote his travelogue. “At about half the distance from Jerusalem we stopped to rest the horses at the Inn of the Good Samaritan, where many curios were purchased. The old inn bears every mark of being on the site of the hostelry to which a kind-hearted Samaritan would have carried a man who had been robbed and wounded and left half dead by the thieves.” Our dear Methodist does not report finding any wounded Samaritans on this part of the trip, but I am sure he would have taken such a person to this very inn. Later he left the carriage to visit the site where Elijah fed the ravens. He does not say if he saw any ravens and what he fed them if he did; nor was there any sign of a chariot in the sky. The heat was rather intolerable; he estimated it at about 150 degrees. Fortunately the group arrived back in Jerusalem in time for lunch.
The goal of the voyage was The World’s Fourth Sunday School Convention, held in Jerusalem for three days in April. “It was replete with interest. For the full report I refer my readers to the ‘Official Report of the Cruise,’ which is to contain stenographic reports of all the lectures, sermons, addresses, etc., including the convention, from the time we left New York, March S, until our return. May 19.” Our stenographic Methodist then lists the number of attendees by nationality, there being 701 Americans out of a grand total 1,526 individuals representing 23 countries, including six from Japan and one from New Zealand. It was an international Sunday School fest not unlike the Mohammedan pilgrimage.
Eventually the host returned to New York. The parting thought in the book is praise of travel.
“The only know the world is to see it, and the present facilities for travel offer every opportunity of reaching even ‘earth’s remotest bound.’ What are you toiling for? Why are you saving money? To buy another farm? to add to your mortgage or bank account ? Of what avail will it all be if you only come to have a plethoric exchequer and a lean intellect ? mind your best capital? Isn’t your mind your best capital? isn’t it worth your while to drop the mad pursuit wealth or pleasure and fit yourself, by travel and observation, to better act your part in life’s soon to be ended?”
Amen to that. The plethoric exchequer would indeed be a sad way to live.
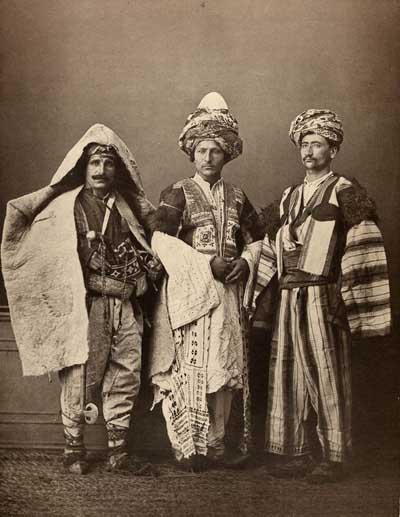
And here is our pilgrim at last: