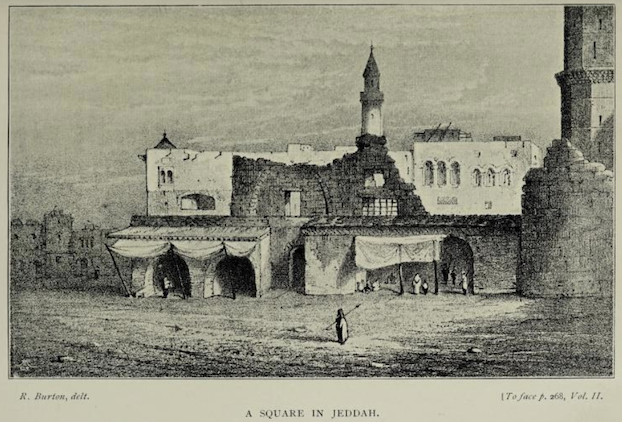
The current de facto ruler of Saudi Arabia, MBS, has promoted a major development scheme entitled Vision 2030. This time, instead of sending henchmen with cleavers, he is authorizing imported Western bulldozers to basically turn the older parts of the historic port of Jeddah into a wannabe Dubai. As noted in a recent article on Qantara:
“Currently, the areas most affected by the destruction are those to the south and east of the old city, the Balad, parts of which have been designated UNESCO World Heritage sites. Prior to evacuation, between 10,000 and 50,000 people lived in each of these neighbourhoods. That means tens of thousands are likely to lose their homes. Estimates circulated by dissidents and demolition critics range from hundreds of thousands to one million."
The port of Jeddah has been the main stopping point for Muslim pilgrims on their way to Mecca for almost fifteen hundred years. It is described by early geographers in detail, given the amount of travelers who passed through. For the modern kingdom, however, history means nothing and can be erased by the whims of the super rich. This continues the destructive Wahhabi impulse that sacked Kerbala in 1802, as described below by ‘Uthman b. Abd Allah b. Bishr (d. 1872) in his Unwan al-Majd fi Tarikh Najd (Mecca, 1930):
“In the year 1802, Ibn Sa’ud made for Karbala with his victorious army, famous pedigree horses, all the settled people and Bedouin of Najd, the people of Janub, Hijaz, Tihama and others…The Muslims [i.e. the Wahhabis] surrounded Karbala and took it by storm. They killed most of the people in the houses and the markets. They destroyed the dome above al-Husayn’s grave. They took away everything they saw in the shrine and near it, including the coverlet decorated with emeralds, sapphires and pearls which covered the grave. They took away everything they found in the town—possessions, arms, clothes, fabric, gold, silver, and precious books. One cannot even enumerate the spoils! They stayed there for just one morning and left after midday, taking away all the possessions. Nearly 2000 people were killed in Karbala.”
When the well-primed news media talk about reform in Saudi Arabia, it is worth noting that reform has a long way to go, given the roots of its blood-soaked Wahhabi past. It will take more than letting women drive at the same time that women who protest are jailed, basic human rights in the kingdom are ignored, and heads are still chopped off in public. Even the chopping up of a journalist who dared to call out the corruption is now ignored, because of the profit for a family which defies the morality of the country’s own Prophet. As long as the Saudi regime buys Western military supplies, they are given free rein to use them, resulting in the world’s worst humanitarian disaster in Yemen, with thousands dead and more dying every day, and fueling the sectarian divide between the Saudis and Iran.
There is a saying that blood is thicker than water, but it seems that for the Saudi elite it is oil which is thicker than either blood or water. They have plenty of oil, have shed lots of blood and are desperate for water. All this leads to an economic domino effect: the world craves oil, oil revenues fuel a family wealth fund which spreads an intolerant interpretation of Islam worldwide, and then much of the oil revenues come back to oil-hungry countries who sell weapons to the Saudis.
Imagine if Greece leveled the Parthenon for a shopping mall and Italy replaced the Colloseum with a football field. In a sense that has already happened to Mecca and Medina. Welcome to Saudi Arabia in 2030…